Why Retrofitting Buildings Is Essential for Net Zero Goals
Achieving global net zero goals isn’t just about building new green structures, it’s about upgrading the ones we already have. Since nearly 70% of today’s buildings will still exist in 2050, retrofitting becomes a major climate strategy. Buildings consume around 40% of global energy and generate 36% of greenhouse gas emissions, largely due to inefficient envelopes, poor insulation, and outdated systems. Older offices, hospitals, and schools lose energy through walls, windows, and air gaps. Smart insulation retrofits offer a fast, cost-effective solution, typically reducing energy use by 20–40%, lowering HVAC loads, and improving comfort all without heavy structural changes.
Smart Insulation: Turning Static Walls into Active Energy Managers
For decades, insulation has been a passive “blanket” it resists heat, but it’s blind to the environment. As we aim for Net Zero and stricter ESG goals, passive resistance isn’t enough. We need walls that think.
Enter Smart Insulation. This technology combines advanced chemistry with digital intelligence to transform your building envelope from a static barrier into an active energy management system.
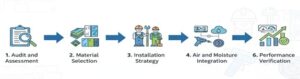
Structure retrofit approach: Efficient results with minimal disruption
Beyond transforming how walls behave, smart insulation also delivers measurable carbon, comfort, and energy benefits proven in real retrofit projects
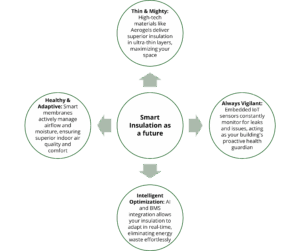
Smart Insulation’s Bigger Impact
Smart insulation helps cut carbon on multiple fronts. It lowers operational carbon by improving thermal efficiency and reducing energy use, and it cuts embodied carbon through durable, recyclable, and bio based materials. Stable indoor temperatures also make renewable systems like solar heat pumps, work more effectively, while sensor data supports transparent ESG reporting.
Real-world projects show strong results: PCM enhanced insulation can reduce cooling energy by 10–41%, and aerogel + PCM retrofits have shown nearly 40% energy savings and 64% lower CO₂ emissions. These upgrades prove that smart materials deliver measurable comfort and carbon benefits.
Globally, the move toward a fabric first approach focuses on improving the building envelope before adding renewables. New trends include hybrid insulation systems, circular materials, and digital twins for accurate energy modeling. With codes like ECBC and ratings such as LEED, BREEAM, GRIHA, and IGBC driving adoption, insulation retrofits are becoming a key step toward low-carbon, climate-resilient buildings.
“Smart insulation doesn’t just save energy, it turns old buildings into intelligent, future-ready climate solutions”
~Kinnari Modi














